-endowment effect inspires us to seek compensation that is equivalent to the pain of losing whatever we have a sense of endowment of. This provides an added level of comfort for first time investors using.

Endowment Effect The Decision Lab
32 The most famous experiment regarding the existence of the endowment effect was conducted by Robert Thaler and his colleagues.
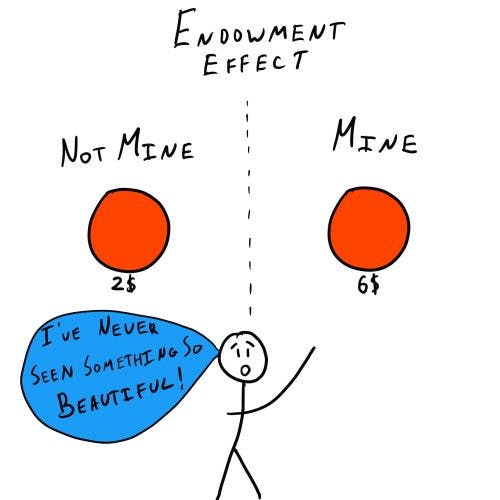
. Registered Investment Advisors have a fiduciary duty to provide advice and investment recommendations that are in the best interests of the client. It states that humans do tend to develop an attachment to the things they have bought and are unwilling to let them go easily much inverse behavior against a rational seller. This endowment effect describes a situation where your price to sell is higher than your willingness to pay.
Definition of the endowment effect. The endowment effect describes the phenomenon where you overvalue things you own simply because those things are yours. Due to the induced-valuation no endowment effect should theoretically exist in a token market.
People behave differently in controlled experiments than they do in the real world. In our next installment of Behavioral Economics 101 we shall explore more examples of the endowment effect at work. Converse allows you to choose the color and design of certain shoes and the act of creation makes you feel like the product has been yours all along.
This automatically becomes an example of the Endowment Effect at work. You are personalizing it and it becomes more difficult to abandon as a result. Sometimes they simply try to fool the experimenter.
The Endowment Effect. Experimenters utilize an induced-valuation technique by assigning varying private redemption values associated with the tokens among individual participants. 25 David Friedmans explanation for the endowment effect is best described by which of the following statements.
The endowment effect describes an innate yet objectively irrational value bias best described by example. The difference between having an opinion on a business decision or a. Making a high price on my dog Grizzly if I had to sell him.
Sometimes they simply try to fool the experimenter. The Endowment Effect tendency can also include biases or opinions as we tend to place a higher value on our opinions because we own them. In psychology and behavioral economics the endowment effect also known as divestiture aversion and related to the mere ownership effect in social psychology is the finding that people are more likely to retain an object they own than acquire that same object when they do not own it.
This is one of the main reasons why the endowment effect is so palpable in finance. Mary for example gets into heated political debates on Facebook while her friend Mark tends to favor his own ideas in business meetings. There are two reasons the endowment effect matters.
So much so that we prefer avoiding a loss of 5 to gaining 5. The ticket therefore takes on a higher value in our ownership. The endowment theory can be defined as an application of prospect theory positing that.
Specifically Thaler used the endowment effect as a means to explain the loss of value associated. Equally the idea that tutoring is the best most cost-effective solution seems predicated on weak cherry-picked evidence ignoring more substantive long-term ideas to help disadvantaged students and improve schools and education. Select It is behavior that is characteristic of only new inexperienced players and will.
1 Thaler RH 1980. Loss aversion like this is the most common explanation for the endowment effect. Put in simple terms the endowment effect is a phenomenon where you overvalue the things you.
People behave differently in controlled experiments than they do in the real world. Endowment effect can be clearly seen with items that have an emotional or symbolic significance to the individual. We hate the idea of losing money on something we own.
Because the endowment effect causes you to overvalue things you own you are more likely to accumulate stuff you dont need and have a hard time parting with it. Once you start looking the endowment effect really is everywhere. We overestimate their real market value and as a result we demand much more to give these things up than we would be willing to pay to acquire them.
In psychology and behavioral economics the endowment effect also known as divestiture aversion and related to the mere ownership effect in social psychology is the hypothesis that people ascribe more value to things merely because they own them. Relying too much on the initial piece of information offered when making decisions. The term endowment effect was coined by Richard Thaler a distinguished theorist of behavioral economics in 1980.
The behavior - defending the things you own - made sense at a time during. Imagine youve just turned 35. Research has identified ownership and loss.
Prospect theory explanation of endowment effect. Endowment effect in behavioral economics is based on the hypothesis that when you own something you wish to sell it at an higher price than youre willing to pay for it. David Friedmans explanation for the endowment effect is best described by which of the following statements.
The axiom that losses loom larger than gains is one of the best-known effects in. The endowment effect has been described as an anomaly in neoclassical theory which predicts that a persons willingness to pay WTP for a good should be equivalent to their willingness to accept WTA payment to be deprived of the same good. Key Takeaways The endowment effect describes a circumstance in which an individual places a higher value on an object that they.
An experimental market commonly employed to gauge the efficiency of market institutions. Journal of Economic Behavior Organization vol vol 1 issue 1 39-60. Youve been proud of the way you hold your liquor since your days in college but have noticed lately that hangovers are rougher than they used to be.
5 He identified this cognitive bias as an explanation for loss aversion a theory outlined by Kahneman and Tversky in 1979. Toward a positive theory of consumer choice. According to behavioral economics and psychology the endowment effect occurs when we attribute greater value to things we own than to things we dont.
As mentioned above the endowment effect can best be described as the phenomenon that people are often willing to sell an item they own for a much higher price than they would be willing to pay for it.

The Endowment Effect Why Ownership Makes You Overvalue Your Things Kent Hendricks

The Endowment Effect Why Ownership Makes You Overvalue Your Things Kent Hendricks

Endowment Effect The Decision Lab

Endowment Effect Https Scienceterms Net Psychology Endowment Effect Psychology Fun Facts Loss Aversion
0 Comments